 |
| Association of Soil Grains |
Now, the relative proportions of those 3 levels play a very powerful position within the engineering conduct of the soil. Those homes are utilized in geotechnical issues like earthworks, and laboratory assessments to compute weights and volumes of the 3 levels.
Let’s talk about the three-phase diagram of soil and essential section relationships utilized in geotechnical engineering calculations.
3-Section Diagram of Soil
Soil is a three-phase subject material composed of air (a), water (w), and soil grains or solids (s) [Fig.2.]. Let’s constitute soil as a section diagram combining all an identical levels as proven in Determine.
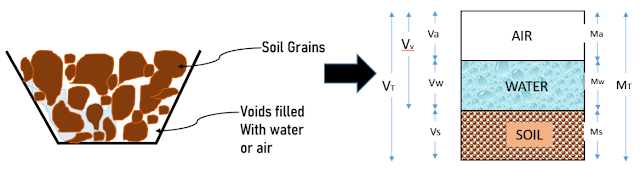 |
| 3-Section Diagram of Soil |
The overall determine represents the three-phase diagram of soil. The quantity of air, water, and soil are Va, Vw, and Vs, whilst the mass is Ma, Mw, and Ms respectively. Right here, we all know that the mass of air Ma = 0.
The General Quantity is the sum of the full quantity of air, water, and soil grains. that provides,
VT
= Va + Vw + Vs;
and the full mass is the sum of the mass of air, water, and soil grains.
MT = Ma + Mw + Ms;
General Quantity of Voids is given as Vv, which is the sum of the amount of air and quantity of water. This implies the voids may also be stuffed both by means of air or water.
Vv = Va + Vw
Let’s to find the members of the family for sure homes of the soil, in line with the three-phase diagram.
1. Void Ratio (e)
The void ratio is the ratio of void quantity (Vv) ratio to the soil grain quantity (Vs). This provides
e = Vv/Vs
Void ratio provides a measure of the amount of voids provide within the soil mass. The upper the void ratio, the upper the presence of voids, and the upper the permeability of the soil. Such soils wish to be compacted ahead of use, particularly for the development of foundations. Or else, below the motion of load, the soil will go through massive deformations.
2. Porosity (n)
The porosity of soil is outlined because the ratio of void quantity (Vv) to the full quantity (Vt). This belongings is expressed in share.
e = Vv/Vt
The porosity varies very much from one roughly soil to some other. The quantity of porosity is dependent upon the minerals that make up the soil and the structural association of the soil grains.
Void ratio and porosity are inter-related and given the system:
e = n / (n-1);
3. Level of Saturation (S)
The level of saturation is outlined because the ratio of the water quantity (Vw) to the void quantity (Vv). It’s expressed in share.
S = Vw/Vv
The level of saturation signifies how extent the empty area of the soil is full of water. When the soil is totally dry, S=0; when the soil is absolutely saturated, S= 100%.
4. Air Content material (a)
Air content material is outlined because the ratio of air quantity (Va) to the amount of the voids. It’s given by means of,
a = Va/Vv;
5. Proportion Air Voids (na)
The share of air voids is given because the ratio of the amount of air (Va) to the full quantity (V). It’s expressed in share.
na= Va/V;
When the soil is absolutely saturated, the proportion of air voids is the same as 0
5 Volumetric Relationships in Soil Engineering
1. Dating Between Porosity (n) and Void Ratio (e)
n = Vv/V
1/n = V/Vv
V = Vv + Vs
Therefore we have now,
1/n = (Vv +Vs)Vv = 1+ (Vs/Vv) = 1 + (1/e) = (1+e)/e
Therefore,
n = e /(1+e)
2. Dating Between Proportion Air Voids (na) and Air Content material (a)
We all know that, the proportion of air voids
na = Va/V
The above relation may also be written as follows by means of
na = (Va/Vv) x (Vv/V)
na = n x ac
The place, na=porosity; a is the air content material








